Dissemination History: This study was presented as an oral presentation in the IZDO 25th International Scientific Congress and Exhibition, 9-11 November 2018, Izmir, Turkey.
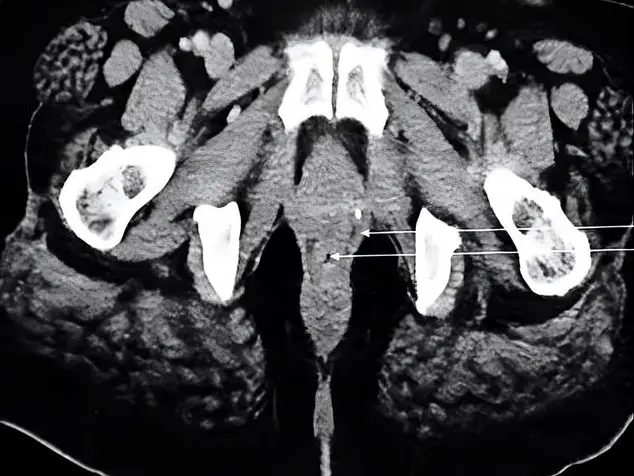
The lateral lingual foramen is an anatomical structure that can be found unilateral or bilateral in the lingual surface of the mandible. The aim of this study is to determine the localization and prevalence of the lateral lingual foramen (LLF) and to evaluate the lateral lingual canal (LLC) using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). CBCT images of 741 patients were examined retrospectively. The prevalence and localization of LLF were assessed by gender and age groups. The distance of the LLF to the mandibular alveolar crest (MAC) and to the inferior border of the mandible (MIB) was measured. The angle of entry of the LLC (LLCA) was also measured. These data were analyzed statistically.
582 LLFs were observed in 396 (53,4%) of 741 patients. LLFs were most frequently observed in the premolar region (87.6%). The mean of the LLF-MAC was 23.28 mm and the mean of the LLF-MIB was 4.71 mm. A statistically significant difference was found in LLF-MAC distance for gender and age groups (p=0.000). This study presented a high prevalence of LLF in the Turkish population. Since the LLF includes inferior alveolar canal or mandibular incisive canal structures, it is necessary to be informed about the existing variations before surgical procedures to prevent complications. Compared to previous studies, higher LLF-MAC distance and lower LLF-MIB distance were observed in the Turkish population. This result can provide confidence in implant applications.