The purpose of the study was to study the morphometric and electron microscopic changes of the parenchyma of the mesenteric lymph nodes of rats under the conditions of action of monosodium glutamate and its abolition. The paper presents and analyzes data from an experimental study conducted on 76 albino rats in females and males of reproductive age. Experimental animals are divided into 5 groups. Eight weeks of exposure to monosodium glutamate (MSG) showed a significant decrease in the relative area of the cortical substance in the parenchyma of the mesenteric lymph nodes of albino rats in males and females by 10.3% and 8.3%, respectively, and an increase in the relative area of the medullary substance by 16.1% and 13.2%, respectively with an intact group of animals. Submicroscopically after eight weeks of exposure to monosodium glutamate, as well as after eight weeks of cancellations, in the parenchyma of lymph nodesintercellular spaces are enlarged, lymphocytes have low electron density, karyolysis, organelles at different stages of decay, the number of macrophages increases, cellular detritus and osmiophilic inclusions in the cytoplasm of macrophages and in the intercellular space. The wall of arterioles is thickened, sclerosed, nuclei of large endothelial cells. There are thorough defects in the capillary wall, venous plethora. The hemocapillary lumen is narrowed due to numerous protrusions and microvilli of the cytolema of endothelial cells. Changes appear after two weeks of action of monosodium glutamate and increase by the eighth week of the experiment. Any changes will not return to normal after cancellation of exposure to monosodium glutamate.
Effects of MSG on the lymph nodes of the albino rat: Ultrastructural and morphometric studies
Tetiana Harapko1, Lesia Mateshuk-Vatseba2
1 Department of Human Anatomy and Histology, Uzhhorod National University, Medical Faculty, Ukraine
2 Department of Normal Anatomy, Lviv National Medical University named after Danylo Halytskyi, Ukraine
SUMMARY
Sign up or Login
INTRODUCTION
One of the most common food additives not only in Ukraine but also worldwide is monomonosodium glutamate (MSG, C5H8NO4NaH2O). This monosodium salt of glutamic acid, often found in nature, exists as free glutamate, and as bound to other amino acids in protein. This food additive belongs to the group of flavor enhancers used in a wide range of products, such as soups, sauces, puddings, chips, meat products and mixed condiments (Hussein et al., 2017; Rutska et al., 2017). However, despite its widespread prevalence, its effect on the body remains insufficiently studied (Zanfirescu et al., 2018). By enhancing the taste of food, monomonosodium glutamate leads to an increase in the amount of food consumed per day, which causes a high-calorie diet (HCD). In studies, the authors describe that HCD leads to metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, diabetes, splenomegaly, hypertension, heart attack, etc. (Buchan et al., 2018; El-Aziz et al., 2018; Kothari et al., 2017).
The results of a study in experimental animals using this additive showed that the consumption of monomonosodium glutamate leads to an increase in lipid peroxidation, nitric oxide, neurotransmitters, accompanied by the accumulation of ß-amyloid peptides in the animal’s body (Hussein et al., 2017). According to other studies, the authors concluded that monomonosodium glutamate leads to obesity (Bautista et al., 2019). It was also found that the addition of monomonosodium glutamate to the diet of rats reduces the excretion of Na, K and water from the body. NaCl retention leads to hypertension, accompanied by renal pathology, intrarenal oxidative stress and decreased nitric oxide secretion (Contini et al., 2017).
An urgent task of modern medicine is to study the effect of dietary supplements, monomonosodium glutamate in particular, on the structure of the parenchyma and the vascular bed of lymphoid (immune) organs. The latter include lymph nodes, which play a role in the body of a kind of biological "filters", whose function is to neutralize antigens, because they themselves are antigen-dependent proliferation and differentiation of T- and B-lymphocytes (Oliveira et al., 2019). Lymphocytes and macrophages are among the major cells involved in the immune response (Arundina et al., 2017; Kusumaningsih et al., 2018). Having studied the features of the structural reorganization of the immune system under the action of monomonosodium glutamate, it becomes possible to study methods for correcting these changes.
The aim of the research was to study the morphometric and electron microscopic changes of the parenchyma of mesenteric lymph nodes of rats under the conditions of action of monosodium glutamate and its abolition.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study was conducted on 76 albino rats of male and female reproductive age (2.5-6.5 months) weighing 120-280 g. The microanatomy of the structural components of the mesenteric lymph nodes of albino rats under physiological norms was examined in 10 intact animals. The experimental animals were divided into 5 groups: the first group (10 animals), who had been on a high calorie diet (HCD) for two weeks; the second (10 animals), the third (10 animals), and the fourth group (10 animals), who had been on HCD for four, six, and eight weeks, respectively; the fifth group (10 animals), who had been on a HCD for eight weeks, followed by a standard vivarium diet for eight weeks. Each group had 5 male rats and 5 female rats. HCD was achieved by adding 0.07 g / kg of rat body weight to food monosodium glutamate.
Controls were served by 16 albino rats who received a standard vivarium diet instead of the high-calorie diet.
All experimental animals were kept in the vivarium of Danilo Halytskyi National Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the provisions of the European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals Used for Experimental and Other Scientific Purposes (Strasbourg, 1986), Council of Europe Directives 86/609 / EEC (1986), Law of Ukraine No. 3447-IV «On the Protection of Animals from Cruelty behavior», the general ethical principles of animal experimentation, approved by the First National Congress of Ukraine on Bioethics (2001).
Before the material was taken, the animals were numbed with anesthesia. The fixation of the mesenteric lymph nodes was performed with a 1.5% solution of osmium tetroxide in 0.2 M monosodium cacodylate solution at pH 7.2 for 2-2.5 hours in the cold. Dehydration in increasing concentrations of ethyl alcohol (50 о, 70 о, 90 о and absolute) for 30 min each and propylene oxide for 10 min. The material was poured into a mixture of epoxy resins and polymerized for 24 h in a thermostat at 60° C. The sections were made on a UMTP-6M ultramicrotome using a diamond knife (DIATOM) and double Reynolds and uranyl acetate were contrasted. Sections of lymph nodes were examined using a TEM - 100 transmission electron microscope. Photo material was documented using a SONY - H9 digital camera.
Morphometric studies were performed at specific times on histological specimens stained with hematoxylin and eosin using VideoTest-5.0, CAARA Image Base, Stepanizer, and Microsoft Exel on a personal computer.
Statistical processing of digital data was performed using Excel software and STATISTICA 6.0 using the parametric method. The numerical values of the parameters are represented by sample averages (M), standard deviation (σ), standard error of the mean (m), Student's t test (t). The results of the calculations were presented in graphical form in histograms using Microsoft Office, indicating confidence intervals at 95% confidence level (p = 0.95).
RESULTS
In animals of intact and control groups, according to our histological studies, the structure of the mesenteric lymph nodes was consistent with the species norm. Externally, the lymph nodes are covered by a connective tissue capsule from which numerous cortical and medullary trabeculae depart deep into the parenchyma of the node. On the cramped part of the node are hila The parenchyma of the lymph node consists of located on the periphery of the cortical substance, and closer to the hilum of the medullary substance. Electron microscopically found that small, medium and large lymphocytes have a typical structure. Small lymphocytes have a diameter of about 6-7 μm, contain a large nucleus and a thin section of the cytoplasm with numerous ribosomes. Medium lymphocytes with a diameter of about 7-9 μm contain a more rounded nucleus with a distinct nucleolus. The cytoplasm contains ribosomes, a granular endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria (Fig. 1). The large lymphocytes (lymphoblast) have a diameter of about 10 μm, the nucleus is filled with euchromatin, the karyolema is flat. The cytoplasm contains mitochondria and ribosomes. Macrophages have a different nucleus shape, with primary and secondary lysosomes in their cytoplasm.
Two weeks after HCD submicroscopic structure of small and medium lymphocytes is typical. Nuclei are of rounded shape, cytoplasm contains organelles (mitochondria, granular endoplasmic reticulum). However, the contours of the nuclear membrane are not equal, the cytoplasmic membrane loses clarity in some areas (Fig. 2). Among unmodified lymphocytes, there are destructively altered cells whose nuclei have pycnosis signs, and mitochondria contain damaged mitochondrial ridges. Reticulo-endothelial cells contain enlarged nuclei and thickened processes. The number of organelles in the cytoplasm is small, the latter partially changed. The vessels of the hemomicrocirculatory bed are somewhat enlarged, full-blooded.
Submicroscopically, after four weeks of HCD, nuclei with apoptosis phenomena were detected in part of the lymphocytes of all populations. Preferably they are in the state of karyorexis or karyolysis. In the cytoplasm are lighted areas, mitochondria are hypertrophied with light matrix. The lumen of the arteries and arterioles is slightly expanded. In relation to the cytoplasm of endothelial cells, their nuclei occupy a large part. On the luminal surface of endothelial cells in the wall of hemocapillaries, the number of microvilli grows, the cariolem forms protrusions. Organelles in the cytoplasm of endothelial cells lose the clarity of the contours. The lumen of the veins and venules is somewhat increased (Fig. 3).
Submicroscopically, after six weeks of HCD, the number of macrophages with a large number of phagosomes increases in the cytoplasm, fragments of damaged lymphocytes and other osmiophilic inclusions. Reticulo-endothelial cells nuclei are enlarged, deformed, cytoplasm contains damaged organelles. The number of lymphocytes with signs of apoptosis is increasing (Fig. 4). In the part of lymphocytes in the nucleus there are no nucleolus, cytoplasm is enlightened, organelles are damaged. The mitochondria with the enlightened matrix, the tubules of the granular endoplasmic reticulum are swollen, dilated. In the lumen and in the wall of the postcapillary venules with high endothelium, a large number of lymphocytes may indicate an increase in the processes of lymphocyte migration into the parenchyma of the lymph node from the blood.
Submicroscopically after eight weeks of HCD, as well as after eight weeks of cancellation, the changes in the parenchyma of the lymph nodes of both male rats and females intercellular spaces are expanded, lymphocytes have low electron density, there is karyolysis, organelles at different stages. The number of macrophages increased, in whose cytoplasm and extracellular spaces a large number of cellular detritus and osmiophilic inclusions are seen. The latter indicates the growth of the process of cell death. The proportion of collagen fibers and microfibrils in the parenchyma of the node increased. The wall of arterioles is thickened, sclerosed, nuclei of large endothelial cells. There are thorough defects in the capillary wall, venous plethora. The hemocapillary lumen is narrowed due to numerous protrusions and microvilli of the cytolema of endothelial cells, in cross section it has a star-shaped shape. Some areas of the hemocapillaries are so narrow that they do not pass blood cells (Fig. 5).
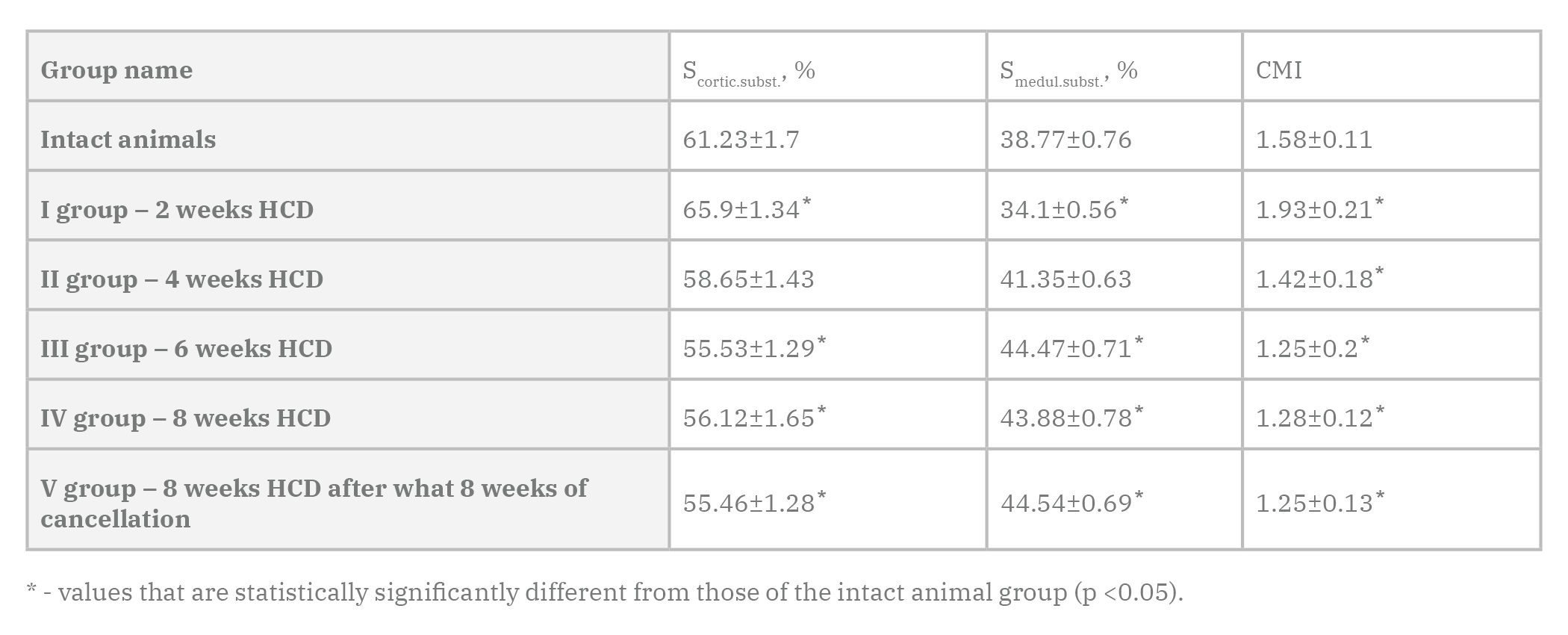
The dynamics of changes in the relative area of cortical and medullary substances and cortical-medullar index (CMI) of lymph nodes of albino male rats in control and experimental groups are expressed in Table 1. Two weeks after HCD, a significant increase in the relative area of cortical substance was shown in the parenchyma of lymph nodes of albino rats of females by 7.6%, compared with the intact group of animals. Accordingly, the relative area of the medullary substance decreases and is 12.0% less than the parameters of the intact group of animals. CMI decreases in female rats by 22.2%.
Four weeks after HCD, a decrease in the relative area of cortical substance was revealed in the parenchyma of lymph nodes of albino rats of females by 11.0%, compared to the previous group of animals, and there were 4.2% less indicators of intact group of animals. Accordingly, the relative area of the medullary substance increases by 21.3% compared to the previous group of animals, and is 6.7% more than the parameters of the intact group of animals. CMI decreases in female rats by 26.4%.
Six weeks after HCD, a decrease in the relative area of the cortical substance was revealed in the parenchyma of lymph nodes of albino rats of females by 5.3%, compared to the previous group of animals, and there were 9.3% less indicators of intact group of animals. Accordingly, the relative area of the medullary substance increases by 7.5% compared to the previous group of animals, and is 14.7% more than the parameters of the intact group of animals. CMI decreases in female rats by 12.0%.
Eight weeks after HCD, an increase in the relative area of the cortical substance was revealed in the parenchyma of lymph nodes of albino rats of females by 1.1%, compared to the previous group of animals, which means 8.3% less parameters of intact group of animals. Accordingly, the relative area of the medullary substance decreases by 1.3% compared to the previous group of animals, and is 13.2% more than the parameters of the intact group of animals. CMI in female rats was 19.0% less than in the intact group of animals.
Eight weeks after HCD, after which 8 weeks of standard vivarium food ration succeeded, a relative decrease in the cortical area was revealed in the parenchyma of lymph nodes of albino rats in females by 1.2%, compared to the previous group of animals, and by 9.4% less than the parameters of the intact group of animals. Accordingly, the relative area of the medullary substance increases by 1.5% compared to the previous group of animals, and is 14.9% more than the parameters of the intact group of animals. СMI in female rats was 20.9% less than in the intact animal group.
DISCUSSION
From studies described in the literature, it is known that the introduction of monomonosodium glutamate at a dose of 30 mg / kg body weight leads to the accumulation in the body of excessive amounts of low and medium molecular weight and reduced ability of the kidneys to excrete toxic products. The shift of markers of intoxication syndrome towards catabolic substances is revealed. One week after the experiment, the results correspond to the phase of partial compensation, which is characterized by an increased concentration of low and medium molecular weight substances in erythrocytes and blood plasma. After two weeks and up to one month of the experiment, catabolic markers of endogenous intoxication predominate, which continue to accumulate in erythrocytes and plasma, indicating a transition to the phase of partial decompensation of all systems and organs involved in detoxification (Krynytska et al., 2019). Based on these results, the organs of the immune system are also affected by intoxication of the body as a side effect of monomonosodium glutamate.
The results of a study conducted on eight-week-old rats on a high-calorie diet showed an increase in blood levels of triglycerides, total cholesterol, low-density lipoproteins, weight gain (De Farias et al., 2019). These are all signs of obesity, which also affects negatively the organs of the immune system.
Similar results are obtained in a study where obesity caused by a high-calorie diet leads to cell death and activation of macrophages in the lymph nodes. The authors concluded that obesity-related inflammation induces lymph node fibrosis and is likely to increase the lumen of the sinuses and subsequently reduce the interaction of immune cells. The resulting effects of immune regulation are likely to contribute to the suppression of immunosuppression and lymphatic dysfunction during obesity (Foster et al., 2017).
The results of a study in which experimental animals received a high-calorie diet that included 20% protein, 20% carbohydrates and 60% fat for two weeks, indicate that the parenchyma of lymph nodes increases the proportion of macrophages and stromal cells that contain lipid inclusions. For comparison, we used a group of animals that received a low-calorie diet that included 20% protein, 70% carbohydrates and 10% fat for two weeks. The authors proved that stromal cells express a large number of genes associated with lipid metabolism, which indicates that lymph nodes are involved in lipid metabolism (Streich et al., 2020).
The novelty of the results described by us is the use of electron microscopic research methods, which gave new data at the ultrastructural level on the structure of lymph nodes under the action of monomonosodium glutamate.
Prospects for further development are related to the study of morphometric and electron microscopic changes in the structural components of rats lymph nodes under conditions of correction of the action of monosodium glutamate.
Conclusions
As a result of a study in rats males and females, we found:
- After eight weeks of action of monosodium glutamate a significant decrease in the relative area of the cortical substance in the parenchyma of lymph nodes of albino rats of males and females respectively, and an increase in the relative area of the medullary substance in comparison with an intact group of animals.
- Electron microscopic сhanges appear after two weeks of action of monosodium glutamate and increase by the eighth week of the experiment. Any changes detected after eight weeks of exposure to monosodium glutamate will not return to normal after cancellation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank all members of Faculty of Medicine, Uzhhorod National University, Lviv National Medical University named after Danylo Halytskyi, Ukraine for their kind cooperation.
Related articles
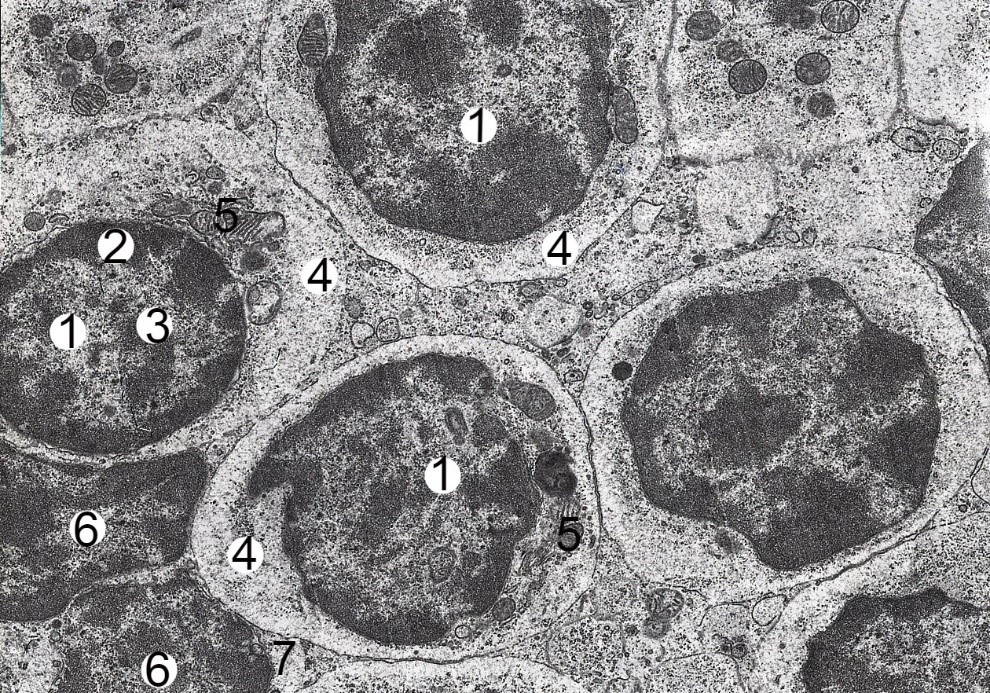 Fig. 1.- Electron-microscopic organization of the cortical substance of the mesenteric lymph node of the albino rat-female intact group. Electronic micrograph. Approx. × 6000. Designation: euchromatin (1), heterochromatin (2) and nucleolus (3) in the nucleus of the middle lymphocyte; the cytoplasm (4) contains ribosomes (5); nucleus (6) and cytoplasm (7) of small lymphocyte.
Fig. 1.- Electron-microscopic organization of the cortical substance of the mesenteric lymph node of the albino rat-female intact group. Electronic micrograph. Approx. × 6000. Designation: euchromatin (1), heterochromatin (2) and nucleolus (3) in the nucleus of the middle lymphocyte; the cytoplasm (4) contains ribosomes (5); nucleus (6) and cytoplasm (7) of small lymphocyte. Fig. 2.- Electron microscopic organization of cortical substance of mesenteric lymph node of albino rat female after two weeks of HCD. Electronic micrograph. Approx. × 6000. Designation: Euchromatin (1) and nucleolus (2) in lymphoblast nucleus, 3 – cytoplasm; nucleus (4) and cytoplasm (5) of middle B-lymphocyte, 6 – osmiophilic inclusions; nucleus (7) and cytoplasm (8) of small B lymphocyte.
Fig. 2.- Electron microscopic organization of cortical substance of mesenteric lymph node of albino rat female after two weeks of HCD. Electronic micrograph. Approx. × 6000. Designation: Euchromatin (1) and nucleolus (2) in lymphoblast nucleus, 3 – cytoplasm; nucleus (4) and cytoplasm (5) of middle B-lymphocyte, 6 – osmiophilic inclusions; nucleus (7) and cytoplasm (8) of small B lymphocyte.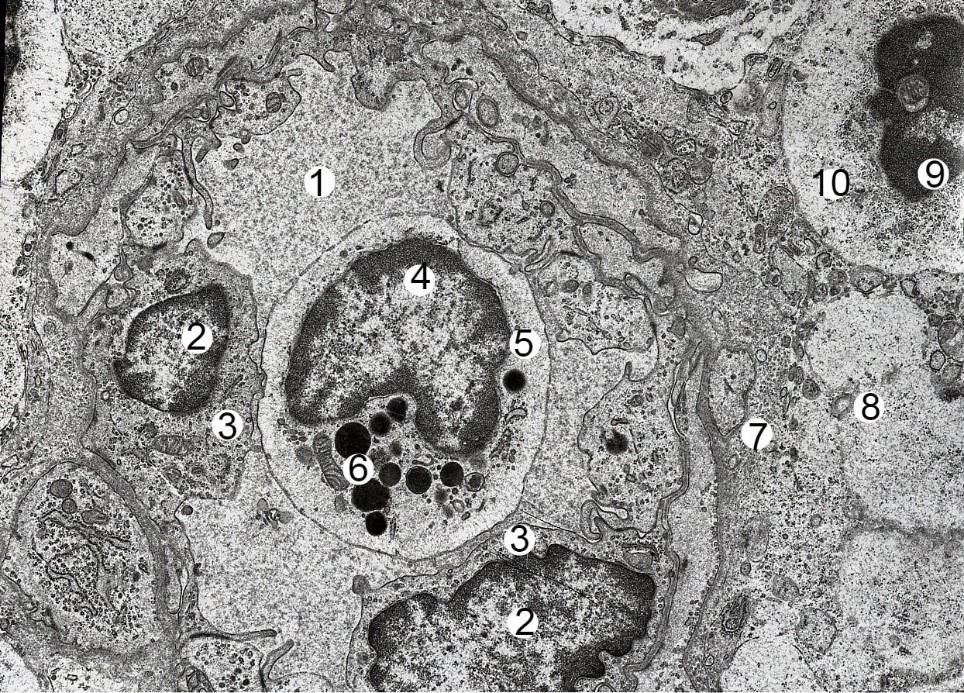 Fig. 3.- Electron microscopic organization of a fragment of a mesenteric lymph node of a albino rat male in four weeks of HCD. Electronic micrograph. Approx. × 6000. Designation: 1 - lumen of the venula; nucleus (2) and cytoplasm (3) of endothelial cells; nucleus (4) and cytoplasm (5) of basophilic leukocyte; 6 – granule; 7 – swollen and thickened basement membrane; 8 – vascular edema; nucleus (9) with signs of apoptosis and cytoplasm (10) of lymphocyte.
Fig. 3.- Electron microscopic organization of a fragment of a mesenteric lymph node of a albino rat male in four weeks of HCD. Electronic micrograph. Approx. × 6000. Designation: 1 - lumen of the venula; nucleus (2) and cytoplasm (3) of endothelial cells; nucleus (4) and cytoplasm (5) of basophilic leukocyte; 6 – granule; 7 – swollen and thickened basement membrane; 8 – vascular edema; nucleus (9) with signs of apoptosis and cytoplasm (10) of lymphocyte.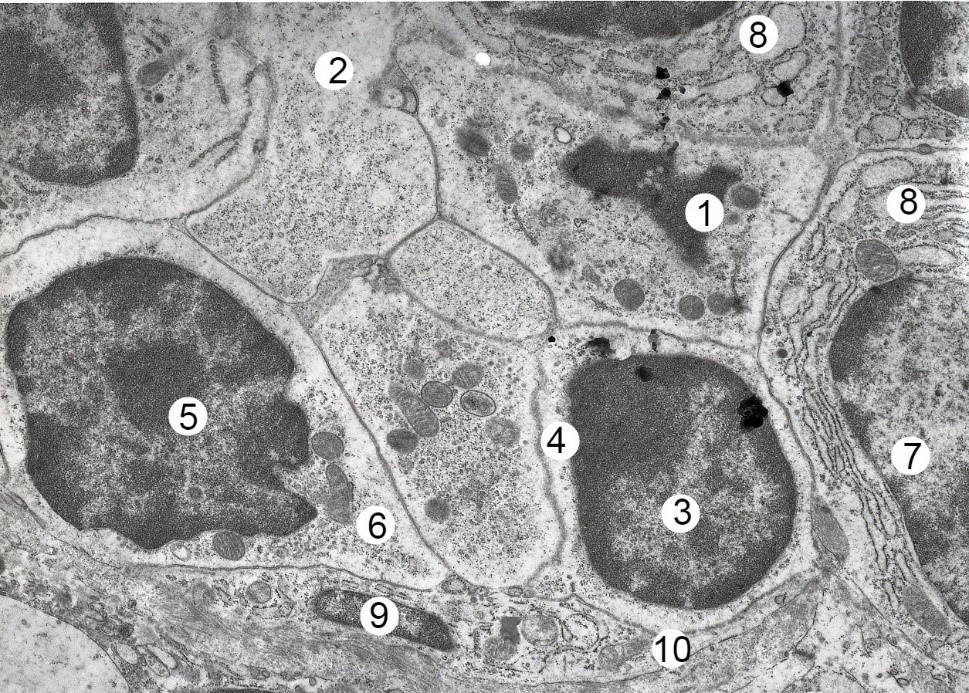 Fig. 4.- Electron-microscopic organization of the cortical substance of the mesenteric lymph node of the albino rat female after six weeks of HCD. Electronic micrograph. Approx. × 6000. Designation: 1 – lymphocyte karyolysis; 2 – destructive area; nucleus (3) and cytoplasm (4) of small B-lymphocyte; nucleus (5) and cytoplasm (6) of middle B lymphocyte; nucleus (7) and cytoplasm (8) of the lymphoblast; 8 – vacuolated cytoplasm of lymphocytes; deformed nucleus (9) and thinned processes of the reticulo-endothelial cells.
Fig. 4.- Electron-microscopic organization of the cortical substance of the mesenteric lymph node of the albino rat female after six weeks of HCD. Electronic micrograph. Approx. × 6000. Designation: 1 – lymphocyte karyolysis; 2 – destructive area; nucleus (3) and cytoplasm (4) of small B-lymphocyte; nucleus (5) and cytoplasm (6) of middle B lymphocyte; nucleus (7) and cytoplasm (8) of the lymphoblast; 8 – vacuolated cytoplasm of lymphocytes; deformed nucleus (9) and thinned processes of the reticulo-endothelial cells.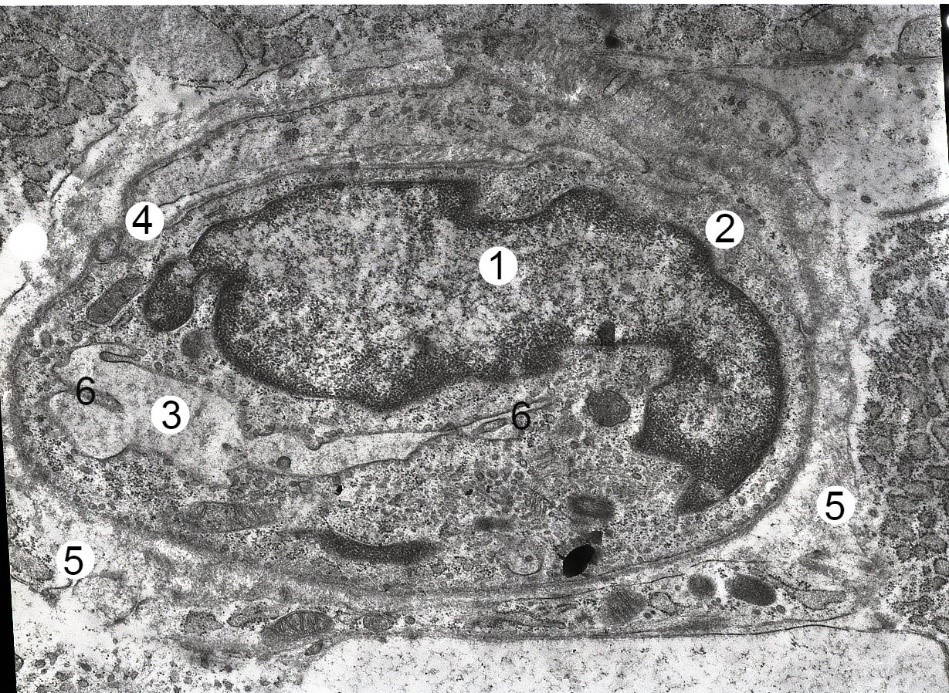 Fig. 5.- Electron microscopic organization of a fragment of a mesenteric lymph node of a albino rat female of reproductive age after eight weeks of HCD. Electronic micrograph. Approx. × 8000. Designation: 1 - deformed endothelial cell nucleus; 2 - cytoplasm of endothelial cells; 3 - narrowed lumen of the hemocapillary; 4 - stratified and swollen basal membrane of the hemocapillary; 5 - vascular edema; 6 – shoots of cytolemy on its luminal surface.
Fig. 5.- Electron microscopic organization of a fragment of a mesenteric lymph node of a albino rat female of reproductive age after eight weeks of HCD. Electronic micrograph. Approx. × 8000. Designation: 1 - deformed endothelial cell nucleus; 2 - cytoplasm of endothelial cells; 3 - narrowed lumen of the hemocapillary; 4 - stratified and swollen basal membrane of the hemocapillary; 5 - vascular edema; 6 – shoots of cytolemy on its luminal surface.ARUNDINA I, DIYATRI I, BUDHY TI, JIT FY (2017) The effect of brotowali stem extract (Tinospora crispa) towards increasing number of lymphocytes in the healing process of traumatic ulcer on diabetic Wistar rat. J Int Dental Med Res, 10(3): 975-980.
BAUTISTA RJH, MAHMOUD AM, KONIGSBERG M, GUERRERO NELD (2019) Obesity: pathophysiology, monomonosodium glutamate-induced model and anti-obesity medicinal plants. Biomed Pharmacother, 111: 503-516.
BUCHAN L, CHAHEYLA R, FISHER A, HELLINGS A, CASTRO M, AL-NAKKASH L, et al. (2018) High-fat, high-sugar diet induces splenomegaly that is ameliorated with exercise and genistein treatment. BMC Res Notes, 11: 752.
CONTINI MC, FABRO A, MILLEN N, BENMELEJ A, MAHIEU S (2017) Adverse effects in kidney function, antioxidant systems and histopathology in rats receiving monomonosodium glutamate diet. Exp Toxicol Pathol, 69(7): 547-556.
DE FARIAS TSM, CRUZ MM, DE SA RCC, SEVERI I, PERUGINI J, SENZACQUA M, CERUTTI SM, GIORDANO A, CINTI S, ALONSO-VALE MIC (2019) Melatonin supplementation decreases hypertrophic obesity and inflammation induced by high-fat diet in mice. Front Endocrinol, 10: 750.
EL-AZIZ R, NAGUIB M, RASHEDB L (2018) Spleen size in patients with metabolic syndrome and its relation to metabolic and inflammatory parameters. Egyptian J Int Med, 30: 78-82.
FOSTER M, VANDERPOOL K (2017) Transmission electron microscopy analysis of visceral and subcutaneous lymph nodes: high fat diet-induced morphological changes. FASEB J, https://www.fasebj.org/doi/abs/10.1096/fasebj.31.1_supplement.lb515.
HUSSEIN U, HASSAN N, ELHALWAGY M, ZAKI A, ABUBAKR H, NAGULAPALLI VK, JANG KY, BISHAYEE A (2017) Ginger and propolis exert neuroprotective effects against monomonosodium glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Molecules, 22(11): 1928.
KOTHARI V, LUO Y, TORNABENE T, O'NEILL AM, GREENE MW, GEETHA T, BABU JR (2017) High fat diet induces brain insulin resistance and cognitive impairment in mice. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1863: 499-508.
KRYNYTSKA I, MARUSHCHAK M, NAUMOVA L, MAZUR L (2019) The toxic impact of monomonosodium glutamate in rats. J Med J, 53(2): 91-101.
KUSUMANINGSIH T, LUTHFI M, MOFFAN MDB (2018) Macrophages analysis on gingival tissue of diabetic rats after insulin leaf extract administration. J Int Dental Med Res, 11(1): 308-311.
OLIVEIRA E, CASTRO S, AYUPE CM, AMBROSIO MGE, DE SOUZA VP, MACEDO GC, FERREIRA AP (2019) Obesity affects peripheral lymphoid organs immune response in murine asthma model. Immunology, 157(3): 268-279.
RUTSKA AV, GETSKO NV, KRYNYTSKA IY (2017) Toxic impact of monosodium glutamate on a living organism. Med Clin Chemistry, (1): 119-127.
STREICH K, SMOCZEK M, HEGERMANN J, DITTRICH-BREIHOLZ O, BORNEMANN M, SIEBERT A, BLEICH A, BUETTNER M (2020) Dietary lipids accumulate in macrophages and stromal cells and change the microarchitecture of mesenteric lymph nodes. J Adv Res, 24: 291-300.
ZANFIRESCU A, CRISTEA AN, NITULESCU GM, VELESCU BS, GRADINARU D (2018) Chronic monomonosodium glutamate administration induced hyperalgesia in mice. Nutrients, 10: 1.